The Future of Urban Planning: Regenerative Design and Ecosystem Biomimicry
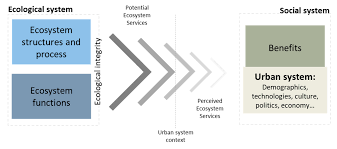
As cities continue to expand and face the challenges of climate change and environmental degradation, a new approach to urban design is emerging – one that looks to nature for inspiration. Regenerative urban design and ecosystem biomimicry are two concepts that offer innovative solutions for creating sustainable, resilient, and harmonious urban environments.
Regenerative Urban Design
Regenerative urban design goes beyond sustainability by aiming to restore and enhance the health of ecosystems within the built environment. It focuses on creating spaces that not only minimise negative impacts but actively contribute to improving ecological functions. By integrating green infrastructure, renewable energy systems, and water management techniques inspired by nature, regenerative urban design seeks to create cities that are in balance with their surrounding ecosystems.
Ecosystem Biomimicry
Ecosystem biomimicry takes inspiration from the natural world to design human-made systems that are regenerative, efficient, and resilient. By studying how ecosystems function and adapt to changing conditions, designers can mimic nature’s strategies to create more sustainable urban environments. From building materials inspired by seashells to transportation systems modelled after ant colonies, ecosystem biomimicry offers a wealth of possibilities for reimagining our cities.
The Benefits
By embracing regenerative urban design and ecosystem biomimicry, cities can reap numerous benefits. These approaches can help mitigate climate change impacts, improve air quality, reduce energy consumption, enhance biodiversity, and promote community well-being. By fostering a deeper connection between humans and nature, regenerative design can create more liveable and resilient cities for future generations.
The Path Forward
As we look towards the future of urban planning, it is clear that regenerative design principles and ecosystem biomimicry will play a crucial role in shaping our cities. By embracing these innovative approaches and working collaboratively across disciplines, we can create urban environments that not only sustain life but actively contribute to its flourishing.
Exploring Regenerative Urban Design and Ecosystem Biomimicry: Key Questions and Insights
- What is regenerative urban design and how does it differ from traditional urban planning?
- How can ecosystem biomimicry be applied to create more sustainable cities?
- What are some successful examples of regenerative urban design projects around the world?
- What role does community engagement play in implementing regenerative design principles in urban areas?
- How do regenerative urban design and ecosystem biomimicry contribute to mitigating the effects of climate change in cities?
What is regenerative urban design and how does it differ from traditional urban planning?
Regenerative urban design represents a paradigm shift in urban planning, moving beyond the conventional focus on sustainability to actively restore and enhance the health of urban ecosystems. Unlike traditional urban planning, which often aims to mitigate negative impacts on the environment, regenerative design seeks to create built environments that function as integral parts of natural systems. By drawing inspiration from nature’s processes and patterns, regenerative urban design integrates green infrastructure, renewable energy systems, and biomimetic strategies to foster resilience and regeneration within cities. This approach not only minimises harm but actively contributes to improving ecological functions, setting a new standard for creating sustainable and thriving urban environments.
How can ecosystem biomimicry be applied to create more sustainable cities?
Ecosystem biomimicry offers a transformative approach to urban design by drawing inspiration from nature’s solutions to create more sustainable cities. By studying how natural ecosystems function and adapt to their environments, designers can mimic these strategies in urban planning. For example, incorporating green roofs inspired by the water retention capabilities of plants can help manage stormwater runoff and reduce the urban heat island effect. Similarly, designing transportation systems that mimic the efficiency of ant colonies can lead to more streamlined and energy-efficient mobility networks. By applying ecosystem biomimicry principles in city planning, we can enhance resilience, promote biodiversity, and improve overall sustainability in urban environments.
What are some successful examples of regenerative urban design projects around the world?
When exploring successful examples of regenerative urban design projects around the world, several notable initiatives stand out. The Bosco Verticale in Milan, Italy, is a pioneering project that features vertical forests integrated into residential towers, promoting biodiversity and improving air quality. The High Line in New York City repurposed an old elevated railway into a vibrant green space that serves as a model for adaptive reuse and urban revitalisation. Additionally, Singapore’s Gardens by the Bay showcases sustainable design principles with its innovative horticultural displays and energy-efficient technologies. These projects demonstrate how regenerative urban design can transform cities into thriving, resilient ecosystems that benefit both people and the environment.
What role does community engagement play in implementing regenerative design principles in urban areas?
Community engagement plays a vital role in implementing regenerative design principles in urban areas. By involving local residents, businesses, and stakeholders in the planning and decision-making process, urban designers can ensure that projects align with the needs and values of the community. Community engagement fosters a sense of ownership and empowerment among residents, leading to greater support and participation in regenerative initiatives. Additionally, by incorporating diverse perspectives and local knowledge, designers can create more inclusive and culturally sensitive urban spaces that resonate with the people who live and work in these environments. Ultimately, community engagement is essential for building sustainable, resilient, and thriving cities that benefit everyone.
How do regenerative urban design and ecosystem biomimicry contribute to mitigating the effects of climate change in cities?
Regenerative urban design and ecosystem biomimicry offer innovative solutions to mitigate the effects of climate change in cities. By incorporating green infrastructure, renewable energy systems, and nature-inspired design principles, regenerative urban design helps reduce carbon emissions, improve air quality, and enhance resilience to extreme weather events. Ecosystem biomimicry takes inspiration from nature’s adaptive strategies to create more sustainable urban systems that can better withstand the impacts of climate change. Together, these approaches not only minimise the environmental footprint of cities but also foster a harmonious relationship between urban areas and their surrounding ecosystems, ultimately contributing to a more climate-resilient future for our cities.