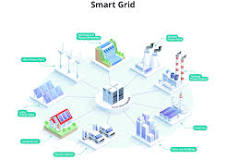
The Future of Energy: Smart Grids
In today’s rapidly evolving world, the demand for energy is constantly increasing. To meet this demand while also ensuring sustainability and efficiency, the concept of smart grids has emerged as a revolutionary solution.
What are Smart Grids?
Smart grids are modern electricity networks that integrate advanced communication and control technologies. These grids enable two-way communication between suppliers and consumers, allowing for real-time monitoring and management of energy distribution.
Benefits of Smart Grids
Smart grids offer a range of benefits that traditional electricity grids cannot match. These include:
- Improved Reliability: Smart grids can detect and respond to outages more quickly, reducing downtime and improving overall reliability.
- Energy Efficiency: By optimising energy distribution and consumption, smart grids help reduce waste and lower energy costs for consumers.
- Integration of Renewable Energy: Smart grids facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power into the grid, promoting sustainability.
- Cybersecurity: With advanced security measures in place, smart grids are more resilient to cyber threats compared to traditional grids.
The Future Outlook
The adoption of smart grids is expected to continue growing as countries worldwide seek to modernise their energy infrastructure. By harnessing the power of data analytics, artificial intelligence, and IoT devices, smart grids will play a crucial role in shaping the future of energy management.
In Conclusion
Smart grids represent a significant step forward in the evolution of energy systems. With their ability to enhance reliability, efficiency, and sustainability, smart grids are poised to revolutionise the way we generate and consume electricity. Embracing this technology is not just a choice but a necessity as we strive towards a greener and more connected future.
Exploring Smart Grids: Global Adoption, Key Benefits, AI Integration, and Device Examples
- What countries have smart grids?
- What are 2 benefits of smart grids?
- Do smart grids use AI?
- What is an example of smart grid device?
What countries have smart grids?
Smart grids have gained significant traction globally, with numerous countries actively implementing and expanding their smart grid infrastructure. Countries at the forefront of smart grid adoption include the United States, Germany, Japan, South Korea, and China. These nations have made substantial investments in modernising their energy networks to incorporate advanced technologies for improved efficiency, reliability, and sustainability. The widespread deployment of smart grids in these countries serves as a testament to the growing importance of embracing innovative solutions to meet the evolving energy needs of the modern world.
What are 2 benefits of smart grids?
Smart grids offer a multitude of advantages, but two key benefits stand out. Firstly, smart grids enhance energy efficiency by optimising the distribution and consumption of electricity, thereby reducing waste and lowering energy costs for consumers. Secondly, smart grids enable the seamless integration of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power into the grid, promoting sustainability and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. These benefits highlight the transformative impact that smart grids can have on modern energy systems, paving the way for a more efficient and environmentally friendly future.
Do smart grids use AI?
Yes, smart grids do utilise artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance their functionality and efficiency. AI plays a crucial role in analysing vast amounts of data generated by the grid, allowing for real-time decision-making and predictive maintenance. By using machine learning algorithms, smart grids can forecast energy demand, optimise energy distribution, and quickly identify potential faults or inefficiencies within the system. This intelligent automation not only improves the reliability and resilience of the grid but also facilitates the integration of renewable energy sources, making energy consumption more sustainable. Overall, AI is an integral component in the evolution of smart grids towards a more efficient and adaptive energy network.
What is an example of smart grid device?
An example of a smart grid device is a smart meter. Smart meters are advanced devices that provide real-time information on energy consumption to both consumers and utility companies. These devices enable users to monitor their electricity usage more accurately and make informed decisions about energy conservation. Smart meters also facilitate two-way communication between consumers and the grid, allowing for more efficient energy management and billing processes. Overall, smart meters are a key component of modernising the electricity infrastructure and promoting sustainable energy practices.