The 14 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a set of 17 global goals adopted by the United Nations in 2015 as part of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. These goals are designed to address a wide range of social, economic, and environmental challenges facing the world today. Each goal has specific targets to be achieved over the next decade to ensure a more sustainable future for all.
Goal 1: No Poverty
End poverty in all its forms everywhere.
Goal 2: Zero Hunger
End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition, and promote sustainable agriculture.
Goal 3: Good Health and Well-being
Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages.
Goal 4: Quality Education
Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all.
Goal 5: Gender Equality
Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls.
Goal 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all.
Goal 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy for all.
Goal 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
Promote sustained, inclusive, and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment, and decent work for all.
Goal 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization, foster innovation.
Goal 10: Reduced Inequality
Reduce inequality within and among countries.
The remaining four goals:
- Sustainable Cities & Communities
- Responsible Consumption & Production
- Climate Action
- Life Below Water & Life on Land
The SDGs represent a universal call to action to end poverty, protect the planet, and ensure that all people enjoy peace and prosperity. By working towards these goals collectively, we can create a more sustainable world for current and future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions about Sustainable Development Goal 14: Life Below Water
- What is SDG goal 14 and 15?
- Why does SDG 14 matter?
- Why does the world need SDG 14?
- What is Goal 14 of SDGs?
- What is SDG 13 14 15?
- How does SDG 14 affect us?
- What is the SDG 14 goal?
- How many targets does SDG 14 have?
What is SDG goal 14 and 15?
Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 14 focuses on “Life Below Water,” aiming to conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas, and marine resources for sustainable development. This goal addresses issues such as marine pollution, overfishing, and the protection of marine ecosystems. SDG 15, on the other hand, is centred around “Life on Land,” with a focus on protecting, restoring, and promoting sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems. This goal aims to combat desertification, restore degraded land, and halt biodiversity loss to ensure a healthy environment for present and future generations.
Why does SDG 14 matter?
SDG 14, which focuses on Life Below Water, is crucial for several reasons. Oceans and marine resources play a vital role in sustaining life on Earth by providing food, regulating the climate, and supporting biodiversity. SDG 14 aims to conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas, and marine resources for sustainable development. By addressing issues such as overfishing, marine pollution, and ocean acidification, SDG 14 not only protects marine ecosystems but also ensures the well-being of millions of people who depend on the ocean for their livelihoods. Achieving SDG 14 is essential for a healthy planet and a sustainable future for all.
Why does the world need SDG 14?
SDG 14, also known as Sustainable Development Goal 14, focuses on conserving and sustainably using the oceans, seas, and marine resources for sustainable development. The world needs SDG 14 because oceans play a crucial role in supporting life on Earth by regulating the climate, providing food and livelihoods for millions of people, and hosting a vast array of biodiversity. However, marine ecosystems are facing unprecedented threats such as overfishing, pollution, and habitat destruction. By implementing SDG 14, countries can work together to protect marine life, promote sustainable fisheries management, reduce marine pollution, and preserve the health of our oceans for future generations.
What is Goal 14 of SDGs?
Goal 14 of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) focuses on “Life Below Water.” This goal aims to conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas, and marine resources for sustainable development. It addresses issues such as marine pollution, overfishing, and ocean acidification, with the ultimate goal of preserving marine biodiversity and ensuring the health and sustainability of our oceans for future generations. Goal 14 highlights the importance of protecting our marine ecosystems and promoting sustainable practices to ensure a healthy and thriving marine environment.
What is SDG 13 14 15?
SDG 13, 14, and 15 refer to the specific Sustainable Development Goals outlined by the United Nations as part of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. SDG 13 focuses on Climate Action, aiming to take urgent measures to combat climate change and its impacts. SDG 14 addresses Life Below Water, aiming to conserve and sustainably use marine resources for sustainable development. Lastly, SDG 15 focuses on Life on Land, aiming to protect, restore, and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, manage forests sustainably, combat desertification, and halt biodiversity loss. These goals highlight the importance of environmental conservation and sustainability for a more resilient and equitable future.
How does SDG 14 affect us?
SDG 14, which focuses on Life Below Water, has a significant impact on all of us. The goal aims to conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas, and marine resources for sustainable development. Our oceans play a crucial role in regulating the Earth’s climate, providing food and livelihoods for millions of people, and supporting biodiversity. By addressing SDG 14, we can ensure the health of our marine ecosystems, protect vulnerable species, and secure the livelihoods of coastal communities. Ultimately, the success of SDG 14 not only benefits the marine environment but also has far-reaching effects on human well-being, economies, and the overall health of our planet.
What is the SDG 14 goal?
SDG 14, also known as Sustainable Development Goal 14, focuses on “Life Below Water.” This goal aims to conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas, and marine resources for sustainable development. SDG 14 targets issues such as marine pollution, overfishing, coastal degradation, and ocean acidification. By promoting the conservation and sustainable management of marine ecosystems, SDG 14 seeks to ensure the health and resilience of our oceans for current and future generations.
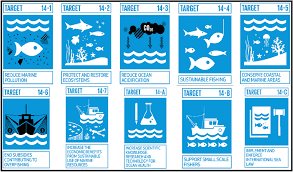
How many targets does SDG 14 have?
SDG 14, which focuses on Life Below Water, has a total of ten targets that aim to conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas, and marine resources for sustainable development. These targets address issues such as marine pollution, overfishing, coastal ecosystems conservation, and sustainable management of marine resources. By setting specific targets within this goal, the international community aims to ensure the health and sustainability of our oceans for future generations.